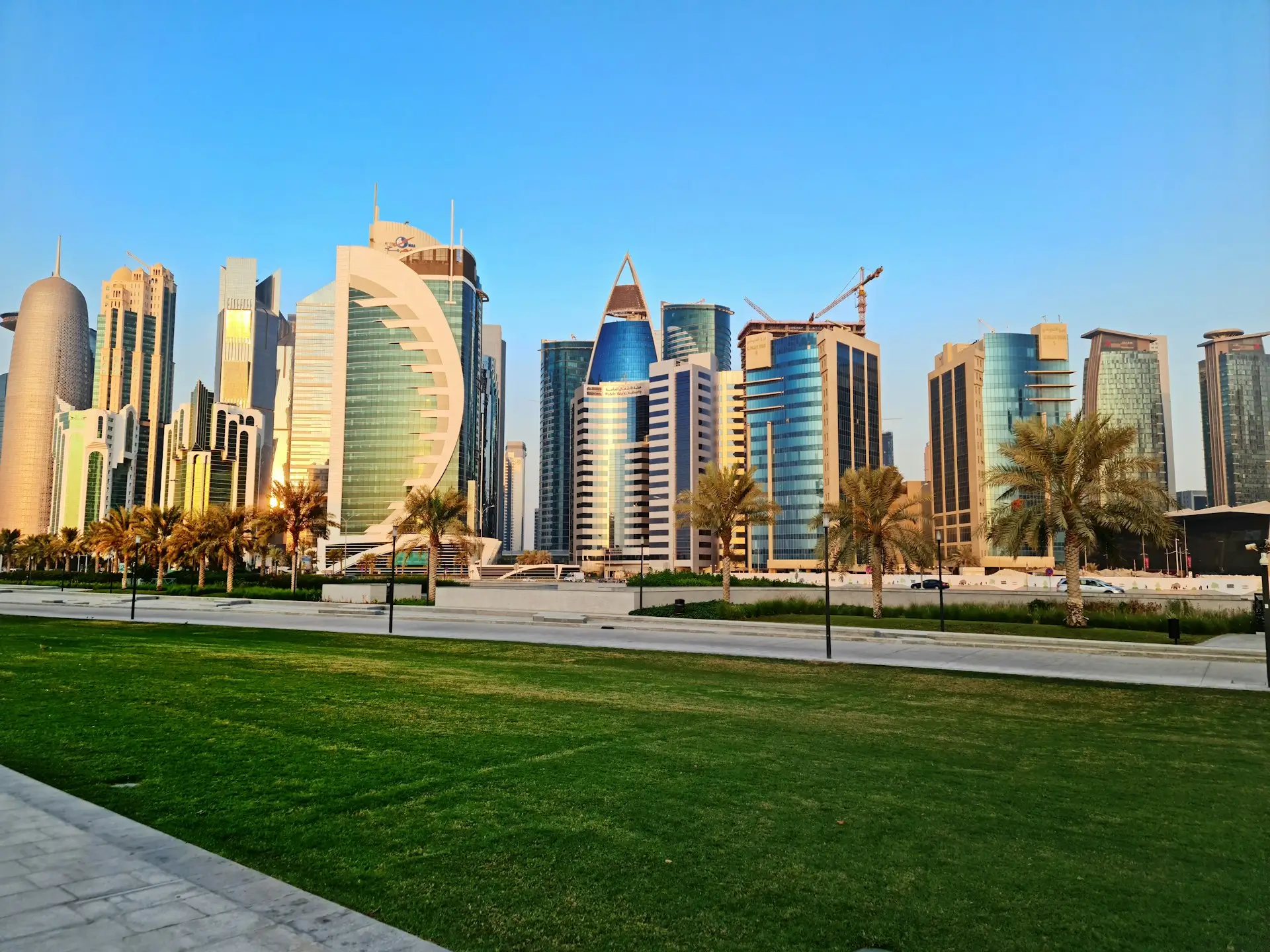


Hire in Qatar
Get your HR processes and recruitment strategies off the ground in Qatar with these essential tips.

Currency of Qatar
Qatari Rial (QAR)
The Capital of Qatar
Doha

Time Zone in Qatar
UTC + 3
Important Facts About the Country of Qatar
Introduction to Qatar
Qatar, officially referred to as the State of Qatar, is situated in Western Asia. Operating as a semi-constitutional monarchy, the nation relies significantly on foreign labor. Migrant workers constitute 86% of the population and 94% of the workforce. Qatar’s impressive economic growth has primarily been driven by its petroleum and natural gas industries, which were established in 1940.
What to Know about Qatar’s Geography
Qatar occupies a compact desert peninsula extending northward from the vast Arabian Peninsula. Covering around 160 kilometers from north to south and 80 kilometers from east to west, it shares its border with eastern Saudi Arabia, connected to the mainland. To the north and west lie the United Arab Emirates, while the island nation of Bahrain is situated approximately 40 kilometers northwest of Qatar.
Climate in Qatar
Between June and September, Qatar endures an intense and humid climate, marked by blistering daytime temperatures peaking at around 50°C. In the milder spring (April and May) and autumn (October and November), temperatures average around 17°C. Winters in Qatar are relatively cooler than other seasons. Rainfall is rare and minimal throughout the region.
The Culture of Qatar
Qatar’s cultural tapestry is woven with the enduring legacy of Bedouin traditions, echoing its nomadic origins and preserving age-old customs. Yet, amidst these deep-rooted traditions, urbanization and coastal living shape modern-day Qatar, blending ancient heritage with contemporary life. Influences from India, East Africa, and neighboring Persian Gulf nations further enrich the cultural mosaic. Renowned for their gracious hospitality and inclusive spirit toward expatriates, Qataris uphold profound reverence for local religious and cultural practices, underscoring their societal fabric.
Religions Observed in Qatar
Islam is the official religion of Qatar, with the majority of Qataris adhering to Sunni Islam. A small minority also follows Shi’a Islam. The ruling Thani family (Al Thani) practices Wahhabi Islam, akin to the rulers of Saudi Arabia. Conversely, Qatar’s non-Qatari population reflects a diverse religious landscape, with Muslims, Christians, and Hindus constituting the largest religious communities in the country.
Languages Spoken in Qatar
Arabic is the official language of Qatar, with most Qataris speaking a Gulf Arabic dialect similar to those spoken in neighboring countries. Modern Standard Arabic is taught in schools, while English is commonly used in diverse settings. Among the significant expatriate population, Persian and Urdu are also frequently spoken languages.
Qatar Human Resources at a Glance
Employment Law Protections in Qatar
Qatar’s legal system comprises two main avenues for implementing laws:
1. The Sharia court, also known as the Islamic court, operates within the framework of Islamic sociocultural norms and adheres to Sharia law.
2. The Adlia courts, or civil courts, were established post-Qatar’s independence to address the legal needs of non-Muslim residents.
The Qatar Labor Law, outlined in Labor Law No. 14 of 2004, sets forth minimum standards for employee rights and benefits, binding both employers and employees.
Article 4 of this law delineates worker protections that employers must adhere to. These include regulations on working hours, provisions for maternity leave, requirements for termination notices, explicit wage structures, and other measures aimed at safeguarding the interests of both employees and employers.
Employment Contracts in Qatar
The Kingdom of the Netherlands comprises four constituent countries: the Netherlands, Aruba, Curaçao, and Sint Maarten. These countries participate as equal partners within the Kingdom, although in reality, the Netherlands predominantly administers most of the Kingdom’s affairs. The Netherlands, as a constituent country, primarily occupies a significant land area in Europe, while its three special municipalities (Bonaire, Saba, and Sint Eustatius) are situated in the Caribbean alongside the other three constituent countries.
All contracts and relevant documents must be written in Arabic as per the requirement. While the employer may furnish copies in additional languages, in the event of any discrepancy or dispute, the Arabic version will carry greater weight. Documentation of the contract in writing is obligatory. Copies should be provided to:
- one copy each for the employer and employee
- one copy for the Ministry of Administrative Development and Social Affairs (MADLSA), also known as the Labor Ministry.
The contract must explicitly delineate the terms of the employment agreement between the two parties involved, encompassing all relevant details such as:
- Employer’s name and workplace
- Worker’s name, qualifications, nationality, profession, residential address, and identification document proof
- Contract date
- Nature and specifics of the job, including the workplace
- Commencement date of employment
Duration of the contract if it’s fixed-term - Salary, benefits, and additional compensations (housing, transportation, meals, etc.)
- Method, date, and frequency of salary disbursement
In June 2020, the Ministry of Administrative Development, Labor, and Social Affairs introduced a digital authentication platform for multilingual employment contracts. This initiative seeks to provide a holistic digital solution for validating employment agreements within organizations, offering an alternative to conventional approaches.
Qatar's Contract Terms
Employment agreements in Qatar can span different durations, ranging from fixed-term to open-ended contracts. Fixed-term contracts are capped at a maximum duration of five years. The terms of each contract, including provisions regarding termination and notice periods, are contingent upon the nature of the agreement.
When renewing a contract for the second or subsequent time, it is crucial for the new agreement to specify the start date of the initial contract. This practice ensures transparency and establishes a clear reference to the previous contractual period.
Pre-Employment Checks
Verification of an employee’s prior employment, medical history, financial standing, and educational qualifications is permissible.
Work Rules in Qatar
Employers in Qatar with a workforce of ten or more employees are obligated to present their work regulations and disciplinary code to the Ministry of Manpower. These regulations must cover essential aspects concerning the rights and obligations of both employer and employee. Such documentation should outline internal reporting structures, procedures for determining and disbursing wages and bonuses, and criteria for internal promotions.
For companies employing 50 or more individuals, the Labor Law stipulates the creation of a complaints and grievance policy, which must gain approval from the Ministry. Any amendments to these policies also require authorization from the Labor Department. In the absence of approval notification within a month of submission, the regulations are deemed approved.
Moreover, these regulations must be conspicuously displayed within the company premises, ensuring easy accessibility and awareness among all employees.
Qatar's Guidelines Regarding Probation Period/Trial Period
The probationary period in Qatar cannot exceed six months, and its terms must be mutually agreed upon by both the employer and the employee. An employee cannot undergo more than one probationary period with the same employer.
If, during the probationary period, it becomes evident that the employee is unable to meet their job requirements, the employer reserves the right to terminate the contract. However, the employer must provide the employee with a minimum notice period of one month. Conversely, the employee also retains the right to terminate the employment during the probationary period by issuing written notice.
In instances where the employee is transferred to another employer, the new employer is obligated to compensate the previous employer for a portion of the recruitment fees and air ticket expenses, up to a maximum of two months’ worth of the employee’s basic wage.
Should an employee serving a probationary period intend to leave the country, they must provide a notice period of two months before their departure.
Regulations and Rules Regarding Working Hours in Qatar
As outlined in the Qatar Labor Law, the standard workweek duration is capped at 48 hours, spread across a maximum of six business days, with each day not exceeding eight hours of work. However, during the holy month of Ramadan, the workweek is shortened to a maximum of 46 hours, with a daily limit of six hours. Additionally, mandatory breaks, lasting from one to three hours, must be provided for prayer, rest, and meals.
Moreover, employees are prohibited from working for more than five consecutive hours. Friday is universally designated as the weekly rest day for all workers, ensuring a day of relaxation and rejuvenation.
Qatar Laws Regarding Overtime
Overtime encompasses any hours worked beyond an employee’s regular working schedule. In such instances, the employee is eligible for extra compensation, comprising their standard wage plus a supplementary payment of no less than 25% for the additional hours worked beyond their usual working hours.
If overtime occurs between 9 p.m. and 4 a.m. on a regular workday, the employee is entitled to their usual wages plus an additional 50% of their wage. In the event of work on a scheduled rest day, the employee is entitled to their standard wages plus an increment of no less than 150%.
It’s crucial to emphasize that the maximum duration for overtime cannot exceed two hours per day.
Timesheets & Record Keeping in Qatar
Payroll reports in Qatar are required to be kept on record for a period of six years.
Rules Regarding Bonus and 13th Month Pay in Qatar
After completing one year of continuous service, employees in Qatar are entitled to receive a bonus equivalent to at least three weeks’ salary for each year of service.
Termination
In Qatar, it is mandatory for an employee to receive three written warnings before facing dismissal, except in cases involving criminal activity, which permit immediate termination.
Employees also possess the right to terminate their employment contract prematurely under certain circumstances. For fixed-term contracts, this requires providing notice, while for open-ended contracts, termination can occur without notifying the employer. Such circumstances include:
1. Employer violation of labor laws, fraudulent activities, or breaches of contractual obligations.
2. Employee engagement in criminal activities.
3. Existence of significant risks to the employee’s safety or health, known to the employer but not addressed.
On the contrary, employers hold the authority to immediately terminate an employee’s contract without notice or payment of end-of-service gratuity (EOSG) in cases of gross misconduct. Examples of such misconduct encompass:
- – Presenting falsified documents.
- – Assuming a false identity or nationality.
- – Inflicting significant financial harm on the employer or divulging confidential information.
Moreover, immediate termination can occur if an employee is found intoxicated or under the influence of drugs during working hours.
If termination occurs without notice, the employer must compensate the employee with an amount equivalent to the basic wage for the notice period or the remaining portion thereof.
In cases of terminations due to economic or structural reasons, the employer must notify the Ministry of Administrative Development, Labor, and Social Affairs at least 15 days in advance. The notification should detail the reasons for termination and the number of affected employees.
Qatar's Requirements Regarding Notice Periods
The notice period varies based on the length of service:
- – For the first two years of service: one month’s notice.
- – For more than two years of service: two months’ notice.
- For workers paid on a daily basis or per work product:
- – For one year or less of service: one week’s notice.
- – For one to five years of service: at least two weeks’ notice.
- – For more than five years of service: at least one month’s notice.
Failure to adhere to notice requirements by employers or employees requires compensation equivalent to the worker’s basic wage for the notice period or the remaining portion thereof. It’s crucial to honor these requirements for a fair transition.
However, departing from the country without adhering to the notice period may result in a labor ban in Qatar for up to one year for foreign workers. This measure aims to enforce compliance with notice obligations and ensure proper labor practices.
Redundancy/Severance Pay in Qatar
The End of Service (EOS) benefit is a financial package granted to employees when their employment ends. Eligibility for EOS requires a minimum of one year of service with the employer, and it’s provided along with any other due payments upon termination.
Nevertheless, employees receiving retirement benefits or enrolled in equivalent schemes offering higher value than EOS are exempt from receiving EOS payments. This measure prevents duplication of compensation for employees already receiving more substantial retirement benefits.
Other Termination Formalities
Upon the conclusion of the employment contract, it falls upon the employer to coordinate the repatriation of the worker either to their country of origin or to a mutually agreed-upon destination.
The repatriation process must be completed within a two-week timeframe following the expiration of the contract. However, should the worker secure new employment in Qatar before departure, the responsibility for repatriation shifts to the new employer.
Furthermore, the departing employee is entitled to the following end-of-service benefits:
- – Gratuity
- – Repatriation ticket, if applicable
- – Payment for the notice period, if applicable
- – Compensation for any accrued but unused leave (vacation)
- – Settlement of any outstanding payments or deductions
Post-Termination Restraints/Restrictive Covenants
To ensure legal validity, any non-compete provision must be explicitly stated within the employment agreement. However, such clauses are limited to a maximum duration of one year.
The primary objective of a non-compete clause is to prohibit employees from participating in activities within the same industry or directly competing with their former employer. Its aim is to safeguard the employer’s interests and mitigate potential adversities resulting from competition.
Fixed Term Contacts for Qatar Employees
If the parties in a fixed-term contract continue their employment beyond its expiry without formalizing a new agreement, it will be inferred that the contract has automatically transitioned into an indefinite term, retaining its original terms and conditions. This presumption applies unless there is a clear agreement indicating otherwise between the parties.
Tax and Social Security Information for Employers in Qatar
Personal Income Tax in Qatar
In Qatar, individual income derived from salaries or wages is exempt from taxation. This implies that employees are not liable to pay taxes on the income they earn through employment within the nation.
Social Security in Qatar
Presently, Qatar’s social security system applies solely to Qatari nationals engaged in the public sector and specific entities outlined by the Council of Ministers at the General Retirement and Social Insurance Authority (GRSIA), such as joint-stock companies. Employees in the private sector are excluded from this system unless they are Qatari nationals employed by these designated entities as per the GRSIA’s directives.
However, recent legislation in the form of Social Insurance Law No. (1) of 2022 is poised to incorporate Qatari nationals in the private sector, unless their employers offer a private pension scheme with superior benefits compared to those provided by the GRSIA.
Exceptions are granted to companies employing Qataris on a temporary basis for less than one year or as independent contractors. Moreover, employers offering retirement plans with better benefits than the social security system are exempt from compulsory participation.
| Salary Cap (QAR) | Employer Contribution (%) | Employee Contribution (%) | Pension (QAR) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Existing | NA | 10.0 | 5.0 | 15,000/Month |
| New | 100,000 | 14.0 | 7.0 | 15,000/Month |
Employers bear the responsibility of deducting monthly contributions, including their own share, and transferring them to the bank account of the General Retirement and Social Insurance Authority (GRSIA) in Qatar. Alongside these contributions, employers must furnish monthly statements containing contributors’ names, payment dates, and the deposited contribution amounts. They are also mandated to inform the GRSIA in Qatar about the contribution details deposited in the bank account each month.
The contributions are made in the local currency of the worker’s country, adhering to the determined schedule of their respective retirement scheme.
Regarding deductions from pay:
Sharia alimony debt takes precedence over all other debts, ensuring its priority in repayment. However, the total alimony debt cannot surpass 35% of the employee’s wage.
When extending a loan to an employee, the employer is prohibited from levying any interest. Furthermore, the employer must not deduct more than 10% from the employee’s wage to settle the loan amount, ensuring a fair and reasonable portion is deducted for repayment purposes.
Important Information for Qatar Employees
Salary Payment
Employee wages and other payments must be disbursed in the local currency, specifically the Qatari currency, and transferred to the employee’s bank account.
For employees on annual or monthly contracts, payments should occur at least once per month. It is obligatory for all employers to process these payments through the Wage Protection System (WPS) within seven days of the due date.
Employees not on annual or monthly contracts should receive wages at least once every two weeks, ensuring consistent and timely compensation.
Qatar’s Wage Protection System (WPS) is an electronic salary transfer mechanism established to streamline the payment of employee salaries in the private sector. This system enables institutions to transfer salaries to their employees through approved financial entities regulated by the Qatar Central Bank.
The primary objective of the WPS is to maintain a comprehensive database managed by the Ministry of Administrative Development, Labor and Social Affairs (MADLSA). This database records wage disbursements made by private sector employers, guaranteeing that employees receive their salaries promptly and in full. The WPS enhances transparency and accountability in wage payments, benefiting both employers and employees alike.
Payslip
Online payslips are allowed.
Annual Leave
After completing at least twelve months of service, employees in Qatar are eligible for paid annual leave. The duration of this leave depends on the length of service, as follows:
- – For employees with less than five years of service: three weeks
- – For employees with more than five years of service: four weeks
The entitlement to annual leave is adjusted based on the employee’s period of service. If an employee hasn’t completed a full year of service, their annual leave will be calculated proportionally.
Employers have the flexibility to carry forward up to half of an employee’s annual leave entitlement for one year, upon receipt of a written request. This option is subject to business needs and requirements.
Sick Leave
After completing three months of employment, employees in Qatar are entitled to sick leave. To qualify for sick leave, the employee must present a medical report from a physician approved by the employer, confirming the illness.
During the initial two weeks of sick leave, the employee is entitled to receive their full wage, equivalent to 100% of their regular pay.
For the subsequent four weeks of sick leave, the employee will be compensated at half their wage, amounting to 50% of their regular pay.
Any extension of sick leave beyond the initial six weeks will be unpaid, meaning the employee will not receive salary during that period.
Upon reaching the end of the 12th week of sick leave, if a physician’s report confirms that the employee is still unable to return to work, the employer may terminate the employee’s service.
It’s worth noting that the specific terms and conditions of sick leave may vary depending on the employment contract, company policies, and relevant laws in Qatar.
Maternity & Parental Leave
Female employees who have completed one year of service are entitled to a paid maternity leave lasting 50 days in Qatar. Out of this period, up to 15 days can be taken before childbirth, while a minimum of 35 days must be taken after delivery.
If additional leave is needed beyond the initial 50 days, it can be arranged with the employer’s agreement, although it will be unpaid.
To request maternity leave, the employee must submit a leave application along with a medical certificate from a licensed physician, indicating the expected delivery date.
If the employee’s health prevents her from returning to work after maternity leave, she may be granted unpaid leave, provided it does not exceed 60 consecutive days and is supported by a medical certificate.
Dismissal or notice during maternity leave is prohibited unless it can be proven that the employee was employed elsewhere during this period, safeguarding female employees’ rights.
Paternity Leave:
There is no legally mandated paternity leave in Qatar, although some employers may offer it at their discretion.
Nursing Care Leave:
Mothers are entitled to one hour of nursing time per working day for up to one year following childbirth.
Special Leave
Employees have the right to take urgent leave, with each instance not exceeding two consecutive days. Moreover, the total number of urgent leave days permitted annually is limited to seven days. This regulation allows employees to attend to immediate personal matters while also setting a reasonable boundary on the frequency of urgent leave taken within a year.
Religious / Pilgrimage Leave
Employees are entitled to a maximum of fifteen days of unpaid leave to undertake the Al-Hajj pilgrimage, but this can only be utilized once during their tenure with the company. To qualify, employees must have completed at least one year of service with the employer.
The allocation of this leave each year will be determined by the employer according to operational needs. Preference for granting this leave will be given to senior employees and those with longer periods of continuous service. This prioritization ensures that employees who have dedicated more time to the company are given precedence in receiving Al-Hajj pilgrimage leave.
Public Holidays
Employees are entitled to paid time off on official public holidays, which include:
- – Eid EI-Fitr: Three days
- – Eid Al-Adha: Three days
- – Independence Day: One day
- – Three working days as determined by the employer
If a public holiday occurs on a non-working day, such as Friday, the employer must provide an extra day off to compensate employees.
Other Leaves
Some types of leave, such as study leave, bereavement leave, and leave for voting, may vary depending on the industry or state of employment. These leaves can be paid, unpaid, or half-paid, and their availability is typically determined by the organization’s policies and practices.
Benefits to the Employee in Qatar
Qatar Statutory Benefits
The Qatar government mandates that both citizens and expatriates receive health insurance coverage through the Hamad Medical Corporation, ensuring access to essential healthcare services.
Employers in Qatar are also required to offer medical insurance to their employees throughout their employment, guaranteeing access to necessary medical care and assistance.
Regarding retirement, death, and disability benefits, specific provisions are contingent upon a minimum period of insured employment of 25 years. Upon reaching retirement age, pensionable earnings are determined based on the average salary earned during the last five years of employment, aiming to provide financial stability and assistance to individuals in diverse life situations.
Rules Regarding Visas and Foreign Workers in Qatar
General Information
Employers seeking to hire non-Qatari nationals must secure permits from the Ministry of Administrative Development, Labor, and Social Affairs. These permits are issued under specific conditions:
1. No qualified Qatari worker registered for the job.
2. The candidate possesses a residence permit.
3. The candidate has no criminal record.
4. The candidate clears a medical examination.
Periodically, the Ministry of Interior may impose restrictions on issuing work permits and residency visas for citizens of certain countries.
Public Holidays Recognized by Qatar in 2024
| Occasion | Date | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | National Sports Day | February 13 |
| 2 | Eid al-Fitr Holiday | April 10-12 |
| 3 | Eid al-Adha Holiday | June 15-17 |
| 4 | National Day | December 18 |
Hire New Talent in Qatar
Our global hiring services enable you to onboard personnel in any country without the financial commitment required to establish a local entity.