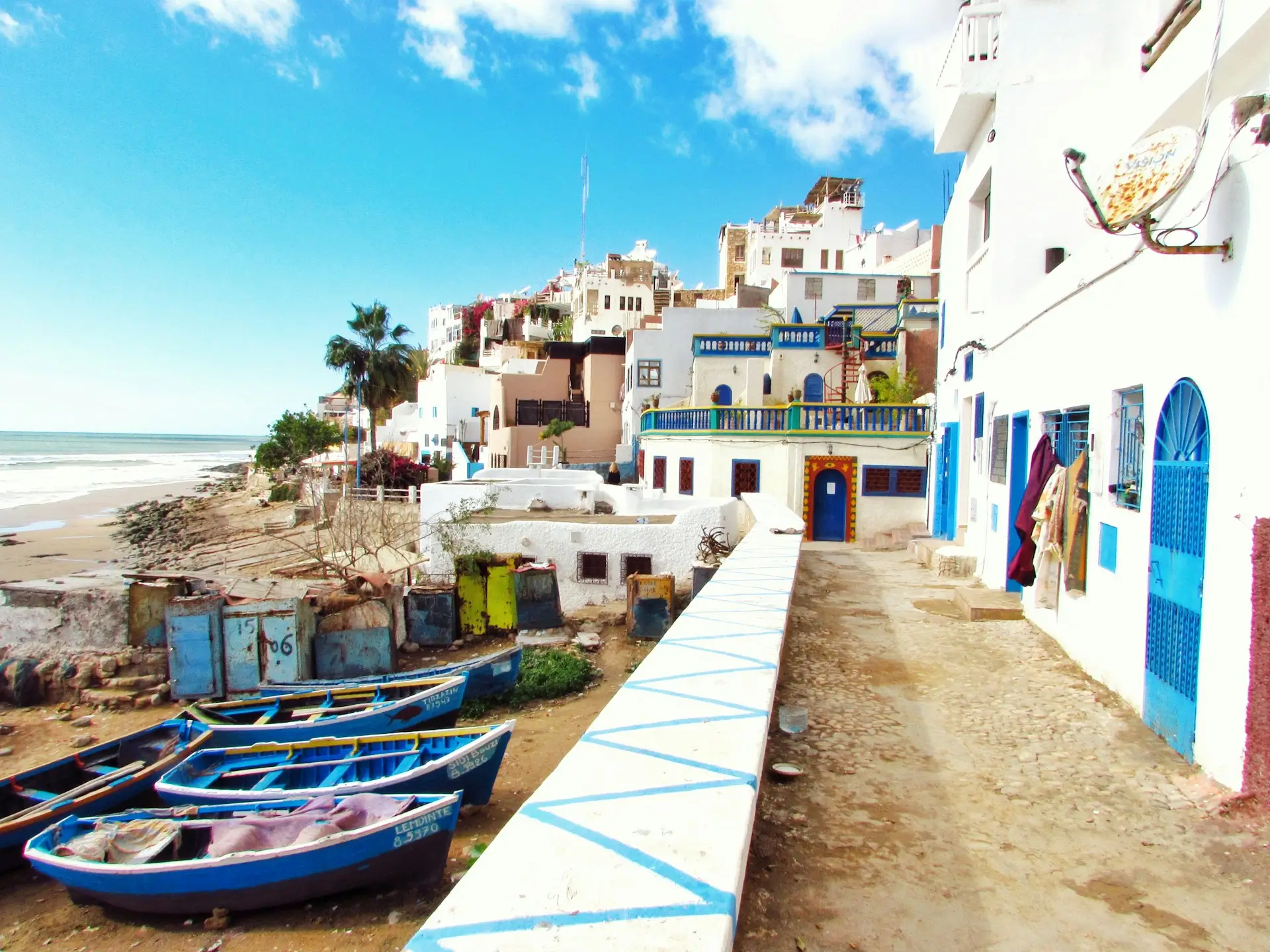

Hire in Morocco
Begin your journey into human resources best practices and recruitment in Morocco right here.

Moroccan Currency
Moroccan Dirham (MAD)
The Capital of Morocco
Rabat

Time Zone in Morocco
GMT+1
Moroccan Human Resources at a Glance
Employment Law Protections in Morocco
The employment relations, both individual and collective, in Morocco are regulated by the Labor Code. Complementing the Labor Code, the government has promulgated several decrees outlining regulations pertaining to fixed-term contracts, notice periods, working hours, and workplace health and safety.
Employment Contracts in Morocco
In Morocco, employers must furnish their employees with written indefinite-term employment contracts (CDI). These contracts are mandated to contain essential details regarding the terms of employment, encompassing:
The employment contract, in adherence to Moroccan regulations, should outline details pertaining to:
- Working hours and the schedule for weekly rest days.
- Timeframes for the payment of wages.
- Industry-specific health and safety regulations.
- Applicable collective agreements.
- Insurance coverage against occupational accidents and illnesses.
In Morocco, the validity of an employment contract hinges on the voluntary capacity of the parties involved in its formation.
Whether for permanent (CDI) or fixed-term contracts (CDD), written documentation is obligatory, with both the employer and employee required to sign the agreement. The contract should exist in duplicate, with one copy retained by the employee.
Important Facts About the Country of Morocco
Introduction to Morocco
Situated in the westernmost part of North Africa, Morocco is officially recognized as the Kingdom of Morocco. The largest city, Casablanca, functions as a key center for industrial and commercial activities with its main port. The capital city, Rabat, is located in the northern region of the country.
What to Know about Morocco’s Geography
Spanning an area of 446,550 square kilometers, Morocco is positioned across the Strait of Gibraltar from Spain. It shares its eastern and southeast borders with Algeria and extends to the south alongside Western Sahara. Morocco boasts a unique geographic feature as the only African country with coastal access to both the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. The Atlantic Ocean aligns its western coast, while the northern part of the country is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea.
Climate in Morocco
Northern Morocco, especially along the coasts, experiences a classic Mediterranean climate in most areas. This entails mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers. The rainy season typically extends from October to April.
The Culture of Morocco
While undergoing rapid modernization, Morocco diligently conserves a substantial portion of its ancient architecture and traditional practices. The country’s culture represents a distinctive fusion of ethnic traditions and religious influences, drawing from Berber, African, Arab, and Jewish heritage. Moroccans are renowned for their tolerant and hospitable demeanor; however, visitors are advised to adhere to modest attire and customary practices such as removing shoes before entering a room.
Religions Observed in Morocco
Islam holds the status of the official state religion in Morocco, with the majority of its population adhering to Sunni Islam. Although Moroccan law ensures freedom of religion, the presence of non-Muslims in the country is limited.
Languages Spoken in Morocco
Arabic holds the official language status in Morocco and is spoken by approximately two-thirds of the population, with the Moroccan dialect Derija being the most prevalent. About 35% of Moroccans communicate in Berber, encompassing various dialects like Tamazight and Rif. French serves as a significant secondary language, especially in business and government, while Spanish is spoken in the northern part of the country. Notably, English is gaining increased prominence in Morocco.
Morocco's Contract Terms
In Morocco, the terms outlined in employment contracts, internal regulations, and collective agreements must, at a minimum, match the provisions specified in the Labor Code. Should these documents offer less favorable conditions, the contracts may be subject to invalidation.
Employers overseeing 10 or more employees are obligated to formulate internal work rules in consultation with employee representatives. These rules should encompass various aspects, including hiring and dismissal procedures, leave policies, absence management, work schedules, and health and safety guidelines.
Every employee in Morocco is required to possess a labor card, containing essential details such as the employer’s information (name, address, and CNSS registration number) and the employee’s particulars like name, date of birth, CNSS registration number, start date, job description, and wage rate. The labor card should be updated whenever there are changes in the employee’s job description or wages.
Fixed Term Contacts for Moroccan Employees
Fixed-term contracts are employment agreements typically with a maximum duration of one year. If such a contract is extended or employment persists beyond the one-year mark, it transitions into an indefinite-term contract. It is mandatory to observe a break between the conclusion of the initial fixed-term contract and the commencement of any subsequent fixed-term contract or extension.
These contracts are generally permissible only under specific circumstances or for certain types of work, such as:
- Temporary replacement of an employee
- Addressing a temporary surge in business activity
- Engaging in seasonal work
Upon the conclusion of a fixed-term employment contract, termination occurs automatically on the expiry date or upon completion of the defined work outlined in the contract. Either party holds the right to terminate the contract immediately during its term in case of misconduct or force majeure. If the contract concludes prematurely, the responsible party for termination is obligated to pay damages equivalent to the agreed-upon wages until the contract’s expiry date. If initiated by the employer, termination requires a minimum two-week notice to the employee.
Employees under fixed-term contracts must utilize their annual leave entitlement before the contract reaches its expiration date.
Pre-Employment Checks
Employees must undergo a medical examination conducted by the occupational doctor before the commencement of their employment or, at the latest, before the conclusion of the probationary period.
Morocco's Guidelines Regarding Probation Period/Trial Period
Probationary periods are optional in Morocco, though they are permissible.
In the case of indefinite-term contracts, the probationary period is constrained to:
- 15 days for blue-collar employees
- one month for white-collar employees
- three months for managers/executive-level employees
An extension of the probation period is allowed only once, for the same duration as initially stipulated.
For fixed-term contracts, the probation period is restricted to:
- one week for contracts lasting less than six months
- one month for contracts lasting six months or more
No extension is permitted for the probation period in fixed-term contracts.
Moroccan Laws Regarding Overtime
Approval for overtime is restricted to instances involving a substantial surge in workload or the execution of urgent work in the public interest. If an employee’s weekly working hours surpass 44 hours, any additional hours are classified as overtime.
The overtime rate is set at 25% for hours worked between the standard working hours (defined as 6 a.m. to 9 p.m.) and escalates to 50% for hours worked outside of these hours (defined as 9 p.m. to 6 a.m.). Furthermore, the overtime rate rises to 100% for hours worked on the employee’s designated weekly rest day.
Moroccan Timesheets & Record Keeping
In adherence to regulations, employers must maintain a comprehensive record of all wages disbursed to employees, which can be documented in either written or electronic format. Moreover, employers are obligated to retain payroll reports for a minimum duration of five years.
Health and Safety in the Workplace
Companies with a workforce of at least 50 employees or those operating in industries prone to occupational illnesses must establish an independent occupational health service. Alternatively, smaller companies have the option to utilize an intercompany or shared service tailored to their industry or location. Irrespective of size, employers bear the responsibility of ensuring their employees undergo medical checkups with the occupational physician:
- Prior to recruitment or, at the latest, before the conclusion of the probationary period.
- Every 12 months during the course of employment.
- Whenever the occupational physician deems it necessary, such as for pregnant female employees, employees with children under the age of two years, employees with disabilities, and those exposed to specific risks.
- Following any sick leave resulting from an occupational accident or illness.
- After repeated health-related absences from work.
Rules Regarding Bonus and 13th Month Pay in Morocco
Workers with a tenure of two years or more are eligible for a seniority bonus, unless otherwise specified in the employment contract, work rules, or a collective agreement.
The seniority bonus constitutes an extra payment, augmenting the employee’s standard wages, and escalates with the duration of service, as outlined below:
| Years of Service | % of Gross Wage |
| >2 | 5.0 |
| >5 | 10.0 |
| >12 | 15.0 |
| >20 | 20.0 |
| >25 | 25.0 |
The computation of the bonus amount encompasses basic wages, overtime supplements, and additional components (such as profit-sharing payments and specific bonuses), excluding tips.
Termination
In the case of employee dismissal due to misconduct, the individual must be afforded an opportunity to present a defense and be heard by the employer or its representative. The employer is obligated to notify the employee of the decision to conduct a hearing within 48 hours of becoming aware of the misconduct. The hearing should be convened within eight days from the employer’s acknowledgment of the misconduct. Comprehensive meeting minutes must be prepared and mutually signed. The employee is entitled to receive a copy, and both parties are expected to cooperate in this process. Failure to cooperate grants either party the right to involve the labor authority.
An employer is only permitted to terminate an employee with an indefinite-term contract for a valid reason, be it related to performance or due to operational requirements of the company.
According to the Labor Code, the following grounds can never serve as valid reasons for dismissal:
- The employee’s race, color, sex, marital status, family responsibilities, religion, political opinions, national descent, or social origin.
- The employee’s disability, unless it hinders the employee from adequately performing the job.
- The employee’s trade union membership or involvement as a trade union representative.
- The employee having filed a complaint or participated in legal proceedings against the employer under the Labor Code.
Morocco's Requirements Regarding Notice Periods
During the probationary period, termination of the contract by either the employer or employee is permissible without providing a specific reason. The employee is not obligated to give notice. If the employer terminates within the initial week of the probationary period, notice is not required. However, beyond the first week, the employer must provide a minimum of two days’ notice for employees paid on a daily, weekly, or fortnightly basis, and eight days’ notice for those paid on a monthly basis, unless the termination results from the employee’s misconduct.
In the event of a female employee being medically certified as pregnant, she has the entitlement to resign without serving notice. For an employee on a fixed-term contract, resignation is possible by compensating the employer.
For an employee with an indefinite-term contract, resignation can occur at any time by adhering to the notice period specified in the employment agreement. This notice, communicated in writing, is determined by the length of their tenure. No severance payment is applicable for voluntary resignations.
The generally accepted notice periods are as follows: [Specify the notice periods as per the original text.]
| Tenure | Executives | Employees/Workers |
| <1 year | 1 month | 8 days |
| 1 – 5 years | 2 months | 1 month |
| > 5 years | 3 months | 2 month2 |
Redundancy/Severance Pay in Morocco
In the event of an unjust dismissal by the company after an employee has completed a minimum of six months of service, they are eligible to receive severance pay. This compensation encompasses remuneration for any untaken annual leave, encompassing the entitlement for the current year and any leave carried forward from the preceding two years. The calculation of severance pay is contingent on the employee’s years of service, as outlined below:
| Tenure | Severance Amount |
| First 5 years | 96 hours of wages per year of service |
| 6 – 10 years | 144 hours of wages per year of service |
| 11 – 15 years | 192 hours of wages per year of service |
| > 15 years | 240 hours of wages per year of service |
Post-Termination Restraints/Restrictive Covenants
In Morocco, the primary categories of enforceable restrictive covenants include confidentiality provisions, non-compete clauses, and exclusivity clauses.
Data Protection
Morocco is governed by Law n° 09-08 of 18 February 2009, a data protection regulation overseen by the Moroccan data protection authority (CNDP). Since the adoption of this law, Morocco has implemented measures to safeguard personal data and align with the data protection standards set by the European Union.
Tax and Social Security Information for Employers in Morocco
Personal Income Tax in Morocco
In Morocco, employees’ earnings are subject to a tax known as ‘Impôt sur le revenu’ (IR), computed using six progressive tax rates spanning from 0% to 38%. Employers have the responsibility to withhold this tax from employees’ monthly payroll, submit their tax returns to the local tax office, and make the payment by the 30th of the subsequent month.
| Annual Taxable Income (MAD) | Tax Rate % |
|---|---|
| 0 to 30,000 | Exempted |
| 30,001 to 50,000 | 10 |
| 50,001 to 60,000 | 20 |
| 60,001 to 80,000 | 30 |
| 80,001 to 180,000 | 34 |
| More than 180,000 | 38 |
Social Security in Morocco
In Morocco, the Caisse Nationale de Sécurité Sociale (CNSS) is the sole mandatory social security regime. While private social security programs are discretionary, employers must collect and remit both their employees’ social security contributions and their own contributions to the CNSS fund.
| Type | Employee Contribution (%) | Employer Contribution (%) | Monthly Salary Limit (MAD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Family allowance | – | 6.40 | No cap |
| Social allocation (Covers short-term, e.g. sickness, maternity & long term e.g. old age, disability pension) | 4.48 | 8.98 | 6,000 |
| Vocational training | – | 1.60 | No cap |
| Mandatory medical care | 2.26 | 4.11 | No cap |
A ‘social solidarity’ contribution is levied on:
- Employers with profits surpassing a specified threshold (ranging from 2.5% to 3.5% of payroll).
- Employees earning an annual income exceeding 120,000 MAD after deductions for Personal Income Tax (PIT) and social contributions (1.5% of pay).
*The provided rates are indicative, and actual rates may vary.
Important Information for Moroccan Employees
Salary Payment
Salaries in India are typically disbursed at the end of the month through bank transfers.
Payslip
Employees must receive payslips containing the following details:
- Employer’s name, address, and CNSS registration number
- Employee’s name, date of birth, and CNSS registration number
- Date of the payslip and the corresponding pay period
- Details of working hours/days worked, including any overtime
- Information on payment in kind or additional compensation
- Gross and net pay, specifying deductions for tax and social security
Electronic payslips are considered acceptable.
Annual Leave
In Morocco, employees are granted 18 days of annual leave per year, equating to 1.5 days of leave per month, provided they have completed a minimum of six months of service. Furthermore, for every five years of service, the entitlement increases by an additional 1.5 days.
| Tenure | Annual Leave |
| > 5 years | 19.5 days |
| > 10 years | 21 days |
| > 15 years | 22.5 days |
| > 20 years | 24 days |
| >25 years | 25.5 days |
| > 30 years | 27 days |
| > 35 years | 28.5 days |
| > 40 years | 30 days (cap) |
To determine an employee’s annual leave entitlement in Morocco, they need to have completed a minimum of one month of work, equivalent to 26 days or 191 hours.
The annual leave is typically expected to be utilized in a continuous block within the year. However, with mutual consent between the employer and employee, it can be taken in shorter intervals or carried forward to the subsequent year. Nonetheless, employees are required to take at least 12 consecutive working days of annual leave along with two rest days.
Sick Leave
To communicate an absence resulting from illness or injury, an employee must notify the employer within 48 hours. In cases where the absence extends beyond four days, the employee is required to furnish a medical certificate, along with an estimate of the anticipated duration of the absence. If an employee remains absent for over 180 consecutive days due to illness or injury, the employer has the prerogative to consider it as a resignation.
For eligibility to sickness benefits from social security, employees insured with CNSS must have made a minimum of 54 days of CNSS contributions in the preceding six months. The benefit amounts to two-thirds of regular wages, capped at a specified ceiling. This benefit becomes payable from the fourth day of absence. While there is no legal obligation for employers to remunerate employees during sick leave, such provisions may be outlined in the employment contract, collective agreement, or internal rules.
Maternity & Parental Leave
Pregnant employees are entitled to a maternity leave period of 14 weeks, commencing no earlier than seven weeks before the anticipated delivery date and concluding no later than seven weeks after childbirth. A medical certificate confirming the pregnancy must be submitted by the employee. In cases where the delivery occurs earlier than expected, any unused prenatal leave can be added to the postnatal leave, ensuring the total duration does not exceed 14 weeks. Female employees are prohibited from engaging in work during the initial seven weeks following childbirth.
Beyond the paid maternity leave, a female employee has the option to take additional, unpaid maternity leave for a maximum duration of 90 days, provided she notifies the employer at least 15 days before the conclusion of the paid maternity leave period. It’s essential to note that no CNSS benefit is disbursed during this supplementary leave.
Breastfeeding breaks
Female employees rejoining the workforce after maternity leave are eligible for paid breaks for breastfeeding, extending for up to 12 months. This entitlement comprises two half-hour breaks daily, one in the morning and one in the afternoon. However, subject to mutual agreement with the employer, the employee can arrange an alternative schedule for these breaks.
If a company employs at least 10 female staff members, the employer is obligated to furnish a dedicated breastfeeding room. This room must adhere to specific statutory requirements and be situated at or in close proximity to the workplace.
Paternity Leave
Other Leave
Employees are entitled to take unpaid leave to attend examinations or participate in national or international sports events.
Public Holidays
Typically, Morocco observes 15 public holidays annually.
Benefits to the Employee in Morocco
Moroccan Statutory Benefits
Participation in the retirement pension system in Morocco is voluntary, with companies opting to affiliate with the Caisse Interprofessionnelle Marocaine de Retraites (CIMR), also known as the interprofessional retirement fund, required to choose one of two CIMR retirement pensions. Employee contributions to the retirement pension are deducted from their wages and must be reflected on their payslips. The employer’s contribution is due within 45 days after the close of each quarter.
On the other hand, work accident insurance is compulsory in Morocco. Employers are obligated to provide coverage to employees against workplace risks, with the estimated premium for white-collar employees standing at 2.7%.
Rules Regarding Visas and Foreign Workers in Morocco
General Information
Foreign nationals, excluding citizens of Algeria, Senegal, and Tunisia, are required to obtain government labor authority authorization to work in Morocco. This authorization is granted through a visa affixed to the employment contract, which is compulsory for foreign nationals and typically takes the form of a fixed-term contract. The visa may be designated for either Expatriate Status (for local hires) or Secondment Status (for intracompany transfers).
The visa acquisition process involves the following steps:
- The employer must declare to the National Agency for the Promotion of Employment and Skills (Agence nationale de promotion de l’emploi et des compétences – ANAPEC) that there are no suitable Moroccan candidates for the position and secure a certificate from the agency.
- The employer must obtain authorization to employ the foreign national by submitting the written employment contract to the Ministry of Labor (via the TAECHIR website). Once approved, the Ministry will review and stamp the contract.
- With the authorized and stamped employment contract, the foreign national can apply for a work visa at the Moroccan embassy or consulate in their country of residence.
- Subsequently, the foreign national may enter Morocco and commence work. Within the initial three months, they must apply for a registration card at a local police station, presenting the stamped employment contract and authorization for employment.
Public Holidays Recognized by Morocco in 2024
| Occasion | Date | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Independence Manifesto Day | January 11 |
| 2 | Eid al-Fitr | April 10 |
| 3 | Labour Day | May 1 |
| 4 | Eid al-Adha | June 17 |
| 5 | Islamic New Year | July 8 |
| 6 | Throne Day | July 30 |
| 7 | Oued Ed-Dahab Day | August 14 |
| 8 | Revolution Day | August 20 |
| 9 | Youth Day | August 21 |
| 10 | Prophet Muhammad’s Birthday | September 15 – 16 |
| 11 | Green March Day | November 6 |
| 12 | Independence Day | November 18 |
Hire New Talent in Morocco
Our global hiring services enable you to onboard personnel in any country without the financial commitment required to establish a local entity.