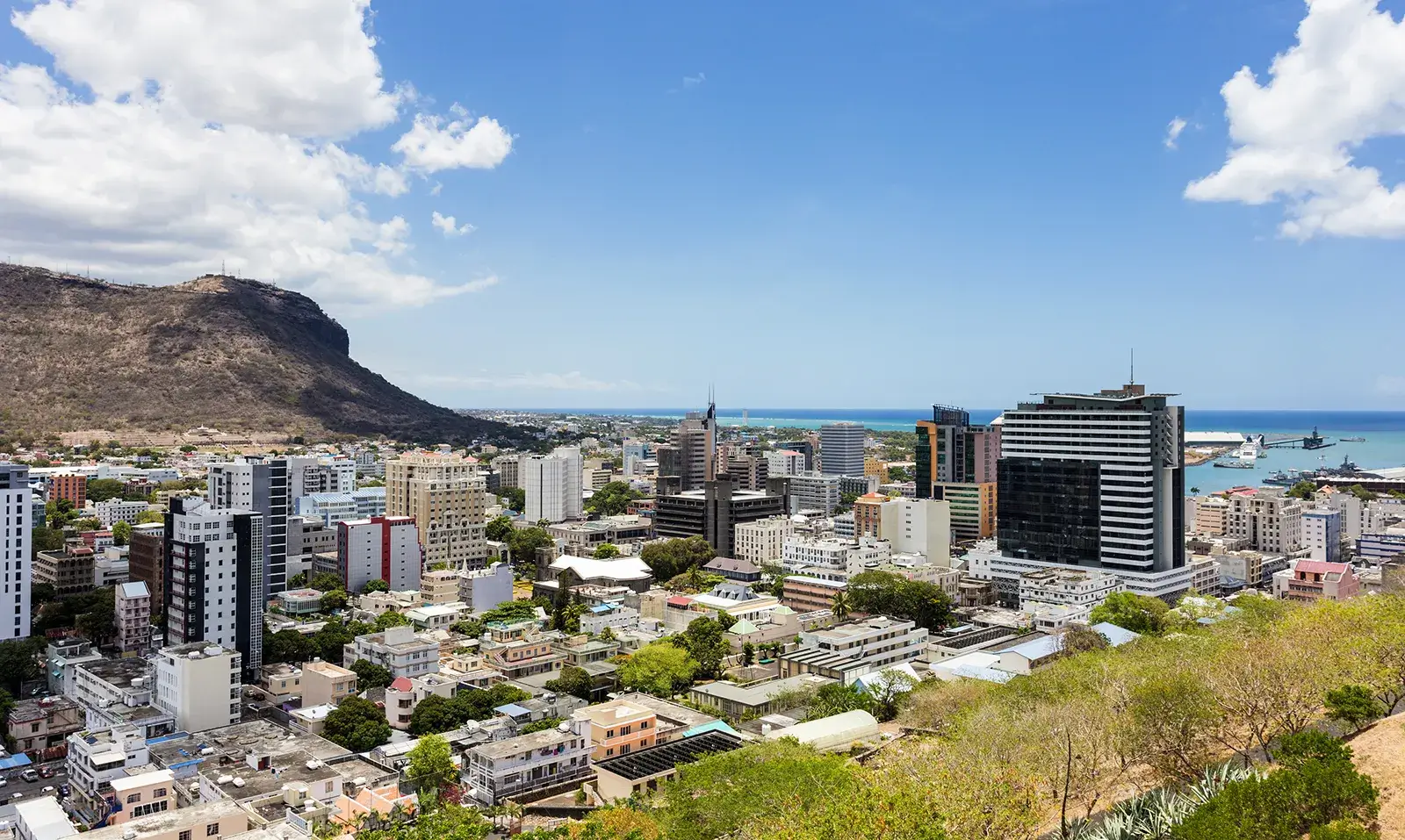


Hire in Mauritius
This is the perfect place to embark on your journey into human resources best practices and recruitment in Mauritius.

Mauritian Currency
Mauritian Rupee (MUR)
The Capital of Mauritius
Port Louis

Time Zone in Mauritius
GMT+4
Important Facts About the Country of Mauritius
Introduction to Mauritius
Mauritius, formally known as the Republic of Mauritius, is situated in the Indian Ocean archipelago roughly 2,400 kilometers away from the eastern coast of Africa, boasting a population of around 1.3 million inhabitants. The nation comprises several islands, namely Mauritius, Rodrigues, Agalega, Tromelin, Cargados Carajos (Saint Brandon), and the Chagos Archipelago (including Diego Garcia). Historically reliant on sugar exports, Mauritius has evolved into a thriving and economically stable nation, emerging as a prominent center for outsourcing and financial services.
What to Know about Mauritius’s Geography
Mauritius’ primary island spans approximately 1,864 square kilometers, measuring roughly 65 kilometers in length and 45 kilometers in width. Characterized by its volcanic origins, the nation is renowned for its picturesque beaches and vibrant reefs.
Climate in Mauritius
Mauritius experiences a maritime subtropical climate, characterized by relatively stable temperatures year-round. Average temperatures range from the mid-70s Fahrenheit (low to mid-20s Celsius) at sea level to the upper 60s Fahrenheit (upper 10s Celsius) on the high plateau. The country recognizes two distinct seasons: the hot season spanning from December to April and the cool season from June to September. Annual rainfall levels vary, with approximately 35 inches (900 millimeters) on the west coast, 60 inches (1,525 millimeters) on the southeast coast, and around 200 inches (5,080 millimeters) on the central plateau.
The Culture of Mauritius
Mauritius boasts a diverse and cosmopolitan culture, reflecting its status as a multi-ethnic and multi-lingual society. Often referred to as a ‘rainbow nation,’ its population predominantly comprises four main ethnic groups. The coexistence of individuals with Indian, African, European, and Chinese heritage has fostered a rich exchange of cultures, values, and collective engagement in festivals. Generally, there is a spirit of understanding and acceptance among people of varying ethnic backgrounds.
Religions Observed in Mauritius
Hinduism holds the largest religious following in Mauritius, with 48.5% of the population adhering to this faith. Roman Catholicism follows closely behind at 26.3%, with Islam constituting 17.30% of the population’s religious affiliation.
Languages Spoken in Mauritius
English and French are widely recognized as the official languages of Mauritius. While the Constitution does not specify an official language, parliamentary proceedings are conducted primarily in English. However, the most commonly spoken language in everyday life is Mauritian Creole, which is based on French and is spoken at home by 86.5% of the population. Other languages spoken include Bhojpuri, Tamil, and various other Indic languages such as Hindi, Telugu, and Urdu. Chinese is also prevalent. The majority of Mauritians are bilingual at a minimum, with many being trilingual or proficient in even more languages.
Mauritian Human Resources at a Glance
Employment Law Protections in Mauritius
The primary legislation governing employment in Mauritius is the Workers’ Rights Act of 2019, which addresses various aspects including:
- Employment contracts
- Minimum age requirements for employment
- Working hours
- Remuneration
- Other fundamental terms and conditions of employment
Additional legislation concerning labor and employment encompasses various areas, including:
- The National Wage Consultative Council Act of 2016, which provides guidance to the relevant Minister regarding national minimum wage standards.
- The Private Pensions Schemes Act of 2012, which regulates the operations of private pension schemes within Mauritius.
- The Employment Relations Act of 2008, governing aspects such as trade unions, workers’ fundamental rights, employers’ rights, collective bargaining, dispute resolution, and related matters.
- The Workers’ Rights (Additional Remuneration) (2020) Regulations 2019, which are annually updated to address the payment of extra remuneration to private sector employees to offset increases in the cost of living or inflation.
The Constitution of Mauritius guarantees various freedoms and rights, including protection against discrimination based on factors such as race, political opinion, country of origin, color, or gender.
Employment Contracts in Mauritius
Under the provisions of the Workers’ Rights Act of 2019, it is mandatory for employers to furnish all employees with a written document outlining the specific terms of their employment. This document must adhere to the format prescribed by the Act and should be provided within 14 days following the completion of the initial calendar month of employment. The statement must encompass the following particulars:
- Employer details
- Employee particulars
- Commencement date of employment
- Workplace location
- Employment details, including category/grade
- Remuneration rate
- Payment frequency
- Standard working hours
However, in the case of fixed-term contracts, the Workers’ Rights Act mandates that employees be provided with written information concerning:
- Specific skills required
- Tasks to be undertaken
- Contract duration
A copy of this statement must be submitted to the supervising officer within 30 days of the commencement of employment.
Important Information for Indian EmployeesImportant Information for Indian Employees
Pre-Employment Checks
Pre-employment checks are subject to certain limitations. Nonetheless, in accordance with the Data Protection Act (DPA), employers gathering personal data from job applicants must secure the candidate’s explicit consent. Moreover, it must be explicitly stated that the processing of such personal data is essential for the purpose of evaluating potential employment opportunities.
Mauritius's Guidelines Regarding Probation Period/Trial Period
The probationary period typically spans from three to six months and may be prolonged provided that the terms of the probation period were established upon finalizing the employment agreement.
In the event that either party desires to terminate the employment before the probationary period concludes, a minimum notice period of 30 days applies (unless otherwise stipulated in the employment contract).
Regulations and Rules Regarding Working Hours in Mauritius
The standard workweek for full-time employees (excluding part-time workers) consists of 45 hours, with allowances made for meal and tea breaks. Here are the specifics:
- For a five-day workweek, employees are required to work nine hours per day over any five days of the week.
- For a six-day workweek, employees work eight hours per day over any five days, with an additional five hours worked on another day of the week (excluding public holidays).
The maximum daily working hours are capped at 12, except under special circumstances and in compliance with other relevant laws.
Employees are entitled to breaks as follows: one-hour meal breaks for every four hours of work, along with at least one 20-minute tea break or two 10-minute tea breaks, all of which are unpaid.
Employers may propose flexitime arrangements to employees, provided they give at least 48 hours’ notice (and the employee isn’t compelled to agree). Conversely, employees can request flexitime, which employers must grant unless there are valid business reasons for refusal (such as an inability to reorganize work or adverse effects on quality or performance).
Mauritian Laws Regarding Overtime
An employee must be notified 24 hours in advance if they are required to work overtime. However, the employee retains the right to decline overtime work, even with the specified notice period.
Overtime compensation on weekdays is set at 1.5 times the regular rate of remuneration for hours worked beyond the standard working hours. Prior to commencing overtime, employees must be given a paid rest period of at least ten minutes.
On public holidays, the overtime rate is double the normal hourly rate for hours worked on that day. For any additional hours worked beyond the standard working hours on a public holiday, the overtime rate is triple the regular hourly rate.
If the standard workday is extended by two hours, or if an employee is required to work for at least 10 hours in a day, the employer must either provide a suitable free meal or pay a meal allowance of MUR 85 per day.
Rules Regarding Bonus and 13th Month Pay in Mauritius
After completing 12 consecutive months of service with an employer, an employee becomes eligible for an annual bonus. This bonus is calculated as one-twelfth of the employee’s annual earnings.
For employees who have worked for only a portion of the calendar year without any breaks in employment, the bonus is determined as one-twelfth of their earnings for that year. A payment amounting to 75% of the anticipated bonus must be disbursed to the employee no later than five working days prior to December 25th. The remaining balance must be settled by the last working day of the month in which the employment concludes.
Resigning employees are entitled to a prorated bonus if they have maintained continuous employment for a minimum of eight months during the year.
Termination
It is strictly prohibited to terminate an employee based on poor performance if such performance is a result of an injury sustained during work.
According to the provisions of the Workers’ Rights Act (WRA), an employer is required to specify the reason for termination. In cases of gross misconduct, an employer may dismiss an employee without notice, provided the employee’s actions constitute a breach of their contractual obligations.
For terminations due to misconduct, the WRA mandates that the employer must offer the employee an opportunity to explain the charges against them. The notice of termination must be provided in writing and delivered to the employee either in person or via registered mail within 10 days of the employer becoming aware of the alleged misconduct.
The employee has the right to request relevant information or documents pertaining to the charges, and the employer must comply. The employee must be given at least seven days’ notice to respond to the charges. Termination must take effect within seven days of the employee responding to the charges.
The WRA prohibits termination based on personal characteristics of the employee (such as race, religion, country of origin, political opinion, or marital status), being on maternity leave, or being a member of a trade union.
Mauritius's Requirements Regarding Notice Periods
Both the employer and employee are obligated to provide a minimum of 30 days’ notice to terminate the employment contract, which can be conveyed verbally or in writing. In cases where the employer initiates termination, they are obliged to furnish the reasons for termination. However, the notice period may vary if stipulated differently within the employment agreement.
Alternatively, either party may opt to compensate the other party with an amount equal to the remuneration the employee would have earned if they had remained employed during the notice period, in lieu of providing notice.
Redundancy/Severance Pay in Mauritius
Severance allowance is granted to employees who have maintained continuous employment for a minimum of 12 consecutive months with the same employer, either under an indeterminate duration contract or through one or more fixed-term contracts with the same employer, provided the employer terminates the contract for reasons outlined in the WRA.
The severance pay amounts to three months’ remuneration for every 12 months of uninterrupted employment, with a minimum employment period of 12 months required to qualify.
In cases where the court determines that severance pay is owed, it has the authority to award interest at a maximum rate of 12% per annum on the amount owed by the employer to the employee.
Post-Termination Restraints/Restrictive Covenants
To validate restrictive covenants, the following conditions must be met:
- They must be limited in both time and geographical scope.
- They cannot unduly hinder the employee’s ability to pursue gainful employment.
- Their primary aim should be to safeguard the employer’s business interests.
While not obligatory, offering financial compensation is recommended. Restrictive covenants should be constrained both geographically and temporally. Typically, a duration of up to one year is deemed reasonable and acceptable.
Fixed Term Contacts for Mauritian Employees
Fixed-term contracts are legally permissible under the following circumstances:
- Undertaking and completing a specific temporary and non-recurring task.
- Engaging in short-term, seasonal, or project-related work or activities.
- Substituting for another employee on approved leave or suspension.
- Providing training purposes.
However, it is unlawful to utilize fixed-term contracts for work of a permanent nature or for roles that are recurrent and permanent in the employer’s regular business operations.
There is no set maximum duration for a fixed-term contract, and they may be extended through written agreement. If there is a gap of no more than 28 days between two fixed-term contracts, the worker is regarded as being under an indefinite-term contract. Additionally, a fixed-term contract lasting over 24 months is considered indefinite.
Workers on fixed-term contracts must receive terms and conditions no less favorable than those of permanent employees performing similar duties and possessing comparable qualifications, skills, or experience.
Health and Safety
Employers with a staff of 10 or more individuals are required to establish suitable provisions for the medical and healthcare requirements of their employees.
Although there are limitations on mandating workers to undergo medical health checks, according to the Data Protection Act (DPA), data concerning an individual’s physical or mental health status falls under the category of ‘special personal data.’ Therefore, employers must obtain explicit consent from employees to access such information.
Data Protection
Enacted on January 15, 2018, the Mauritius Data Protection Act of 2017 (DPA) replaces the previous 2004 legislation, governing individuals’ privacy rights concerning the collection, processing, storage, transfer, and management of personal data. Aligned with international standards, particularly the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the DPA seeks to modernize Mauritius’ data protection framework.
Tax and Social Security Information for Employers in Mauritius
Personal Income Tax in Mauritius
All earnings from employment, encompassing salary, bonuses, overtime, commissions, and fringe benefits, are subject to taxation. Allowances for housing, education, and other purposes are also considered taxable income.
Under the Pay As You Earn (PAYE) system, employers deduct a withholding tax at the source each month and remit it to the Mauritius Revenue Authority (MRA). At the conclusion of each tax year, employers are required to furnish employees with a “Certificate of Emoluments.” This document details the PAYE tax deductions made at the source, enabling employees to file their personal income tax returns with the MRA.
For the fiscal year 2023-2024, the applicable progressive tax rates are as follows:
| Chargeable Income | Tax Rate % |
|---|---|
| First Rs 390,000 | 0 |
| Next Rs 40,000 | 2% |
| Next Rs 40,000 | 4% |
| Next Rs 60,000 | 6% |
| Next Rs 60,000 | 8% |
| Next Rs 300,000 | 10% |
| Next Rs 300,000 | 12% |
| Next Rs 300,000 | 14% |
| Next Rs 400,000 | 16% |
| Next Rs 500,000 | 18% |
| On the remainder | 20% |
Social Security in Mauritius
Employers are required to submit social security payments within 20 days following the conclusion of the month for which the contribution is due. However, if filed electronically through the Mauritius Revenue Authority (MRA) portal, the deadline extends to one month after the end of the relevant month.
| Type | ER Contribution (%) | EE Contribution (%) |
|---|---|---|
| National Saving Fund (NSF) | 2.5 | 1.0 |
| HRDC Training Levy | 1% for employees whose basic wage does not exceed Rs 10,000 and 1.5% whose basic wage exceeds Rs 10,000 | NA |
| Portable Retirement Gratuity Fund (PRGF) | 4.5 | NA |
| Contribution Sociale Generalisee | 3% on monthly salary not exceeding Rs 50,000; 6% on monthly salary exceeding Rs 50,000 | 1.5% on monthly salary not exceding Rs 50,000; 3% on monthly salary Exceeding Rs 50,000 |
Non-citizen employees who do not qualify as tax residents or hold premium visas are exempt from contributing to the National Savings Fund, HRDC Training Levy, and Contribution Sociale Généralisée.
Important Information for Mauritian Employees
Salary Payment
Employees must receive their remuneration at least once every month. However, employers have the option to pay employees on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis, which is considered acceptable under the law.
Payslip
The employer must provide the employee with a payslip when remuneration is paid. Electronic payslips are permitted and considered valid.
Timesheets & Record Keeping
In accordance with Section 153 of the Income Tax Act 1995, records of employee remuneration must be retained for a minimum of five years. Additionally, a company’s payroll records should be preserved for a period of 10 years.
Annual Leave
An employee who maintains continuous employment with the same employer for 12 consecutive months is entitled to 22 working days of annual leave for each subsequent 12-month period of continuous employment.
For employees who sustain continuous employment with the same employer for six consecutive months without any breaks, they are entitled to one day of annual leave for each subsequent month, up to a maximum of six days’ annual leave by the twelfth month.
Annual leave may be taken as a full day, half day, or for a shorter period as agreed upon by both the employer and the employee. Employees are required to provide at least 48 hours’ notice if they wish to take more than one consecutive day of annual leave.
If an employee is unable to utilize all of their entitled leave days, they shall be compensated with their normal day’s wage for each unused day of leave at the end of the 12-month consecutive period.
In cases where the employer and employee cannot reach an agreement on the timing of leave, half of the leave period must be determined by the employer, while the other half is determined by the employee. However, employers are not permitted to withhold leave from employees without reasonable cause.
Sick Leave
An employee who maintains continuous employment with the same employer for 12 months is eligible for 15 working days of sick leave with full pay.
For employees who sustain continuous employment with the same employer for six consecutive months without any absences, they are entitled to one day of sick leave for each subsequent month, up to a maximum of six days’ sick leave by the twelfth month.
Employees are required to notify their employer of their illness on the first day of absence unless they are unable to reasonably do so.
If an employee remains ill for more than three consecutive working days, a medical certificate is necessary from the fourth day of absence.
Leave of Absence
- Leave for Jury Duty: Employers must provide paid leave to employees during their absence to serve as jurors.
- Leave for Participation in International Sports Events
- Leave for Court Attendance
Compassionate & Bereavement Leave
Bereavement Leave
Employees who have completed 12 months of continuous service with the same employer are entitled to three working days of leave upon the death of their spouse, child, father, mother, brother, or sister.
Marriage Leave
Employees who have maintained 12 months of uninterrupted employment with the same employer are eligible for the following special paid leave benefits:
- Six working days’ leave for their own marriage (only applicable for their first civil or religious marriage).
- Three working days’ leave for the first civil or religious marriage of their child.
Maternity & Parental Leave
Maternity leave
A female employee who has maintained continuous employment with an employer for 12 consecutive months is granted 14 weeks of maternity leave. This leave can commence before the birth, provided that at least seven weeks are taken immediately after the birth.
If the employee does not fulfill the requirement of having 12 months of continuous employment, she is still entitled to maternity leave, albeit without pay.
In the case of a stillborn child, a female employee is entitled to 14 weeks of maternity leave with full pay upon submission of a medical certificate, regardless of her length of employment. Similarly, if a female employee experiences a miscarriage, as confirmed by a medical practitioner, she is entitled to three weeks of leave with full pay.
Breastfeeding Break
Public Holidays
Mauritius observes a total of 15 annual public holidays. Among these, seven are fixed holidays, occurring on January 1 and January 2, February 1, March 12, May 1, November 2, and December 25.
The remaining public holidays are religious festivals, and their dates vary each year.
Benefits to the Employee in Mauritius
Mauritian Statutory Benefits
The Workers’ Rights Act 2019 introduced the Portable Retirement Gratuity Fund (PRGF). This fund disburses a retirement gratuity to employees who retire at or after the age of 60, or under circumstances outlined in the law. Employers are relieved of the obligation to provide any retirement gratuity to their employees.
Additionally, the Workfare Programme Fund offers financial aid to working-aged citizens experiencing unemployment. Within the Workfare Program, there exists an optional scheme known as the Transition Unemployment Benefit (TUB), accessible to working-aged citizens (excluding part-time workers, migrant workers, or non-citizens) in the private sector. TUB is provided for a duration ranging from one to twelve months. Its funding is shared among the employee, the employer, and the government.
Eligibility for citizens entails termination of employment due to economic or structural reasons affecting the business, or unlawful termination, misconduct, or poor performance. To qualify, the claimant must have worked for their most recent employer for a minimum of six months and must register with the Workfare Program within seven days of dismissal.
Other Benefits
Transport Allowance
If the distance between an employee’s residence and their workplace exceeds three kilometers, the employer must either provide free transport or reimburse the equivalent of the return fare.
In cases where the employee needs to start or end work at times when public bus or light rail services are unavailable, the employer is obligated to provide free transport.
If the distance between an employee’s residence and their workplace exceeds three kilometers, and the employee commutes using their own transportation with the employer’s approval, the employer must compensate them with the equivalent of the return bus or light rail fare.
Petrol Allowance
Effective from July 1, 2023, if an employer provides a petrol allowance to an employee, the allowance must be at least Rs 1,000 more than it was in December 2021.
Rules Regarding Visas and Foreign Workers in Mauritius
General Information
The employment of expatriates in Mauritius is governed by the Non-Citizens (Employment Restriction) Act 1973, requiring non-citizens to possess a valid work permit before engaging in any employment within Mauritius.
While there are no inherent legal barriers to employing foreigners, obtaining a work permit hinges on demonstrating that the requisite skills are unavailable among the local workforce at the time of application.
Public Holidays Recognized by Mauritius in 2024
| Occasion | Date | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | New Year’s Day | January 1 |
| 2 | New Year Holiday | January 2 |
| 3 | Thaipoosam Cavadee | January 25 |
| 4 | Abolition of Slavery | February 1 |
| 5 | Chinese Spring Festival | February 10 |
| 6 | Maha Shivaratree | March 8 |
| 7 | Independence and Republic Day | March 12 |
| 8 | Ugaadi | April 9 |
| 9 | Eid al-Fitr* | April 10 |
| 10 | Labour Day | May 1 |
| 11 | Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary | August 15 |
| 12 | Ganesh Chaturthi | September 8 |
| 13 | Divali | October 31 |
| 14 | Arrival of Indentured Labourers | November 2 |
| 15 | Christmas Day | December 25 |
Religious holidays are confirmed closer to the date as they rely on the sighting of the moon.
Hire New Talent in Mauritius
Our global hiring services enable you to onboard personnel in any country without the financial commitment required to establish a local entity.