

Hire in Jordan
Begin your journey into human resources best practices and recruitment in Jordan right here.

Jordanian Currency
Jordanian Dinar (JOD)
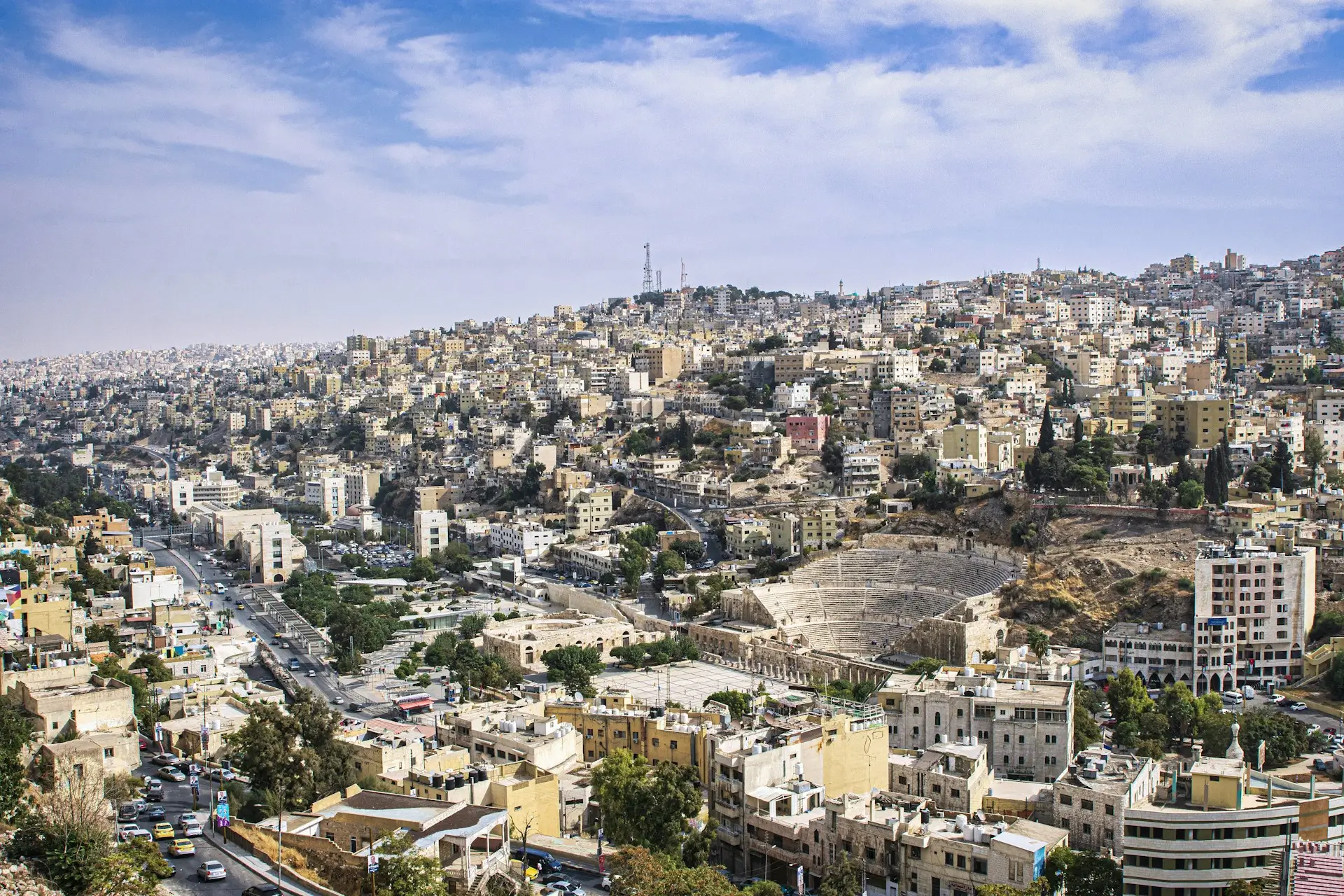
The Capital of Jordan
Amman

Time Zone in Jordan
GMT+3
Important Facts About the Country of Jordan
Introduction to Jordan
Jordan, officially recognized as the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is situated in Western Asia. Positioned on the eastern bank of the Jordan River, it holds a strategic location at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe. Serving as the nation’s capital, Amman is not only its largest city but also a crucial hub for economic, political, and cultural activities. With a population of around 10 million people, Jordan stands as the eleventh most populous Arab nation. The country operates under a constitutional monarchy system, where the king possesses significant executive and legislative powers. Jordan is a founding member of the Arab League and the Organization for Islamic Cooperation, establishing itself as an upper-middle-income economy.
What to Know about Jordan’s Geography
Jordan is surrounded by neighboring countries on multiple fronts. To the south and east, it shares borders with Saudi Arabia. Iraq forms its northeastern boundary, while Syria borders it to the north. On the western side, Jordan is surrounded by the Palestinian West Bank, Israel, and the Dead Sea. Furthermore, Jordan features a 26-kilometer coastline along the Gulf of Aqaba, part of the Red Sea, creating a natural separation from Egypt. In total, Jordan’s land area encompasses approximately 89,000 square kilometers.
Climate in Jordan
Jordan encounters a remarkably diverse climate featuring pronounced seasonal changes. The summer months, spanning from May to September, exhibit scorching and arid conditions, with temperatures occasionally reaching over 40 °C, especially in July and August. In contrast, the winter period, stretching from November to March, brings milder temperatures averaging around 11 °C. Some elevated western regions experience regular rainfall and occasional snowfall during winters, imparting a wintry charm to the landscape.
The Culture of Jordan
Jordan is deeply intertwined with the Arab world, embracing its rich cultural heritage. Central to Jordanian society is the family unit, which serves as its focal point. Village life is shaped by the importance of the extended family, agriculture, and hospitality. Conversely, urban Jordanians exhibit a keen appreciation for various facets of modern culture, ranging from musical concerts to operas and ballet performances.
Religions Observed in Jordan
The religious composition of Jordan is predominantly influenced by Sunni Islam, which is the predominant faith embraced by roughly 95% of the population. Alongside the Sunni majority, smaller communities of Ahmadi Muslims and Shiites contribute to the country’s religious diversity. Noteworthy is Jordan’s historical association with some of the world’s oldest Christian communities. Currently, Christians make up around 4% of the population, emphasizing the coexistence of diverse religious beliefs within the nation’s social fabric.
Languages Spoken in Jordan
Modern Standard Arabic is the official language of Jordan. Nevertheless, in daily interactions, a majority of Jordanians communicate using one of the non-standard Arabic dialects, commonly referred to as Jordanian Arabic. Despite lacking official status, English has become widely utilized throughout the country. It functions as the de facto language in commerce and banking, playing a crucial role in facilitating effective communication across various aspects of life.
Jordanian Human Resources at a Glance
Employment Law Protections in Jordan
The foundation of employment regulations in Jordan is the Labor Law of 1996, along with subsequent amendments. This comprehensive legislation addresses a wide range of labor-related matters across the country, serving as the primary legal framework governing employment relationships. Its provisions apply to individuals falling within defined categories of employees and employers. Apart from the Labor Law, other significant legal frameworks also contribute to shaping the employment landscape in Jordan:
- The Jordanian Constitution
- Act No. 56 of 1996 regarding labor inspection
- Industrial Accidents and Occupational Diseases Instructions of 1993
Act No. 19 of 2001 on social security
Employment Contracts in Jordan
In Jordan, employment contracts are required to be prepared in both English and Arabic, although translations are becoming less common nowadays. In the absence of such an agreement, employees retain the right to utilize any legal evidence to assert their entitlements.
According to the law, a written employment contract must include the following details:
- Indication of whether the contract is for an indefinite period or has a specific duration, with the precise timeframe specified in the latter case.
- Specification of the number of copies of the contract to be provided and the languages in which it should be presented.
- Clear details about the salaries to be paid to the employee. If the salary is not explicitly stated, the employee is entitled to receive compensation comparable to that of individuals performing similar work.
- A comprehensive outline of the employee’s duties, responsibilities, position, and the nature of the work they will be engaged in.
- The primary location or principal place of employment, along with any provisions regarding the employer’s right to alter such a location.
- Information about the probationary period, if applicable.
Fixed Term Contacts for Jordanian Employees
In Jordan, employment contracts fall into two categories: indefinite or definite. Fixed-term contracts can have a maximum duration of five years, with no restrictions on renewals. However, if a fixed-term contract reaches its expiration without a renewal clause or termination by either party, it automatically converts into an indefinite-term contract, extending indefinitely.
If an employer chooses not to renew a fixed-term contract, they must give the employee a written notice period of 30 days. If the contract specifies a longer notice period, the employer must comply with that duration accordingly.
Pre-Employment Checks
Jordanian law allows pre-employment checks.
Jordan's Guidelines Regarding Probation Period/Trial Period
The probationary period shall not exceed three months in any case.
Throughout the probation period, the employer retains the right to terminate the employee’s employment without prior notification or any compensation.
Upon the successful completion of the probationary period and continuous employment, the employee’s contract will transition to indefinite status. The probationary period will then be included as part of the employee’s total service duration.
Regulations and Rules Regarding Working Hours in Jordan
In a six-day workweek, the legal working time is established at 48 hours, excluding designated rest and meal breaks. Employees are entitled to a paid weekly holiday on the seventh day.
In Jordan, private businesses often designate Friday as their weekend holiday, whereas banks and government offices typically close on both Fridays and Saturdays.
Eligibility for annual leave varies by location, and workers may carry over their annual leave; however, the accumulation of earned leave is typically capped at a maximum of 45 days.
If an employment contract expires before a worker can take their annual leave, compensation for the leave is calculated proportionately based on the number of months worked and the number of working hours per week.
Jordanian Laws Regarding Overtime
Work hours beyond the standard 48 hours per week must be remunerated as overtime, in accordance with the stipulations outlined in the employment contract or collective agreements. Typically, overtime pay is calculated at a rate of 120% of the regular salary.
Furthermore, when an employee works on their designated weekly day off or during religious or official holidays, they are entitled to additional compensation, with a minimum rate set at 150% of their usual pay.
Jordanian Timesheets & Record Keeping
While there is no legal obligation for employers to maintain attendance records, it is advisable to adopt this practice.
Termination
According to Section 21 of Jordan’s Labor Code, the termination of an employment contract can occur under the following circumstances:
- The contract’s term has expired, or the designated task has been completed.
- The employee passes away or becomes unable to work due to disease or disability.
- The death of an employer, unless the contract specifically accounted for the employer’s personality, does not lead to the termination of the employment contract.
The Jordanian Labor Code distinguishes between ordinary termination (with notice) and extraordinary termination (without notice).
**Ordinary Termination:**
Written notice must be provided by either the employer or employee at least one month before the desired last day.
If the employer gives notice, they may or may not release the employee from employment during the notice term, except for the final seven days.
The employee is entitled to their salary throughout the notice period.
Employees leaving before the end of the notice period, on their own initiative, are not entitled to pay during that time and must compensate the employer with an amount equivalent to their wages during that period.
If the employment agreement is for a fixed term, it may be terminated before that time by either party for reasons specified in Section 29 of the Code, including differences in work, change of residence circumstances, or medical reasons. In such cases, the employee retains entitlement to all benefits and provisions outlined in the contract. Damages may be sought by the employer if the termination is initiated by the worker for reasons not mentioned above.
Employees are protected against dismissal under the following circumstances:
- Authorized holidays, sick leave, or maternity leave.
- Pregnant employees in their sixth month of pregnancy or beyond.
- During the military service period.
Terminated employees can file a complaint with the labor court for unfair dismissal. If successful, they may be reinstated or receive compensation equal to half a month’s salary for each year of employment (a minimum of two months’ salaries). Additionally, they may be entitled to notice pay, severance pay, and other benefits.
Jordan's Requirements Regarding Notice Periods
During the probationary period, the employer has the authority to terminate the employee’s employment contract without the necessity for prior notice or compensation.
Upon the completion of the probation period, if the employer decides to terminate the employee’s contract, they are obligated to provide written notice at least 30 days in advance. This notice remains irrevocable unless both parties mutually agree.
However, specific situations outlined in labor law, such as employee misconduct, may exempt the employer from the requirement of prior notice. Instances of such misconduct include unexplained absences exceeding 20 days.
In case of termination, the employer can choose to release the employee from work during the notice period or mandate their continued employment, excluding the final seven days. Irrespective of the work arrangement during the notice period, the employer is obliged to remunerate the employee’s wages throughout this duration.
Redundancy/Severance Pay in Jordan
Upon termination, the employee is entitled to receive severance pay equal to 50% of their total salary for each year of service. The calculation will be derived from their most recent salary, ensuring a minimum of two months’ salary as a guaranteed amount.
The precise figures for termination payment and severance pay will adhere to the prevailing Jordanian law applicable at the time of termination.
Post-Termination Restraints/Restrictive Covenants
Post-termination restrictions are permissible in Jordan, as long as they adhere to the following general principles:
- The restriction covenant does not extend beyond what is essential to safeguard the legitimate business interests of the corporation.
- The restrictive covenant is reasonable concerning both territory and duration.
Tax and Social Security Information for Employers in Jordan
Personal Income Tax in Jordan
In Jordan, taxes are imposed on all individuals, irrespective of their residency status, for any income earned within the country from taxable activities. These activities encompass employment, business (as a sole proprietor or partner), rental income, and directors’ fees.
The personal income tax rates are determined by the annual taxable income and adhere to a progressive structure with the following rates:
| Annual Taxable Income (JOD) | Tax Rate % |
|---|---|
| Up to 5,000 | 5% |
| 5,001 – 10,000 | 10% |
| 10,001 – 15,000 | 15% |
| 15,001 – 20,000 | 20% |
| 20,001 – 1,000,000 | 25% |
| Over 1,000,000 | 30% |
Social Security in Jordan
Jordan’s social security system is overseen by the Social Security Corporation. This system requires contributions from both employers and employees, with calculations based on the employee’s monthly gross salary.
Employers are obligated to deduct and remit the following social insurance contributions for employees, determined by the employee’s monthly salary:
| Type | Employer Contribution Rate | Employee Contribution Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Pension | 11% | 6.5% |
| Sickness and Maternity | 0.75% | 0 |
| Worker Injury | 2% | 0 |
| Unemployment | 0.5% | 1% |
| Total | 14.25% | 7.5% |