
The Algeria
Begin your journey into human resources best practices and recruitment in Algeria right here.

Algerian Currency
Algerian Dinar (DZD)
The Capital of Algeria
Algiers

Time Zone in Algeria
GMT + 1
Important Facts About the Country of Algeria
Introduction to Algeria
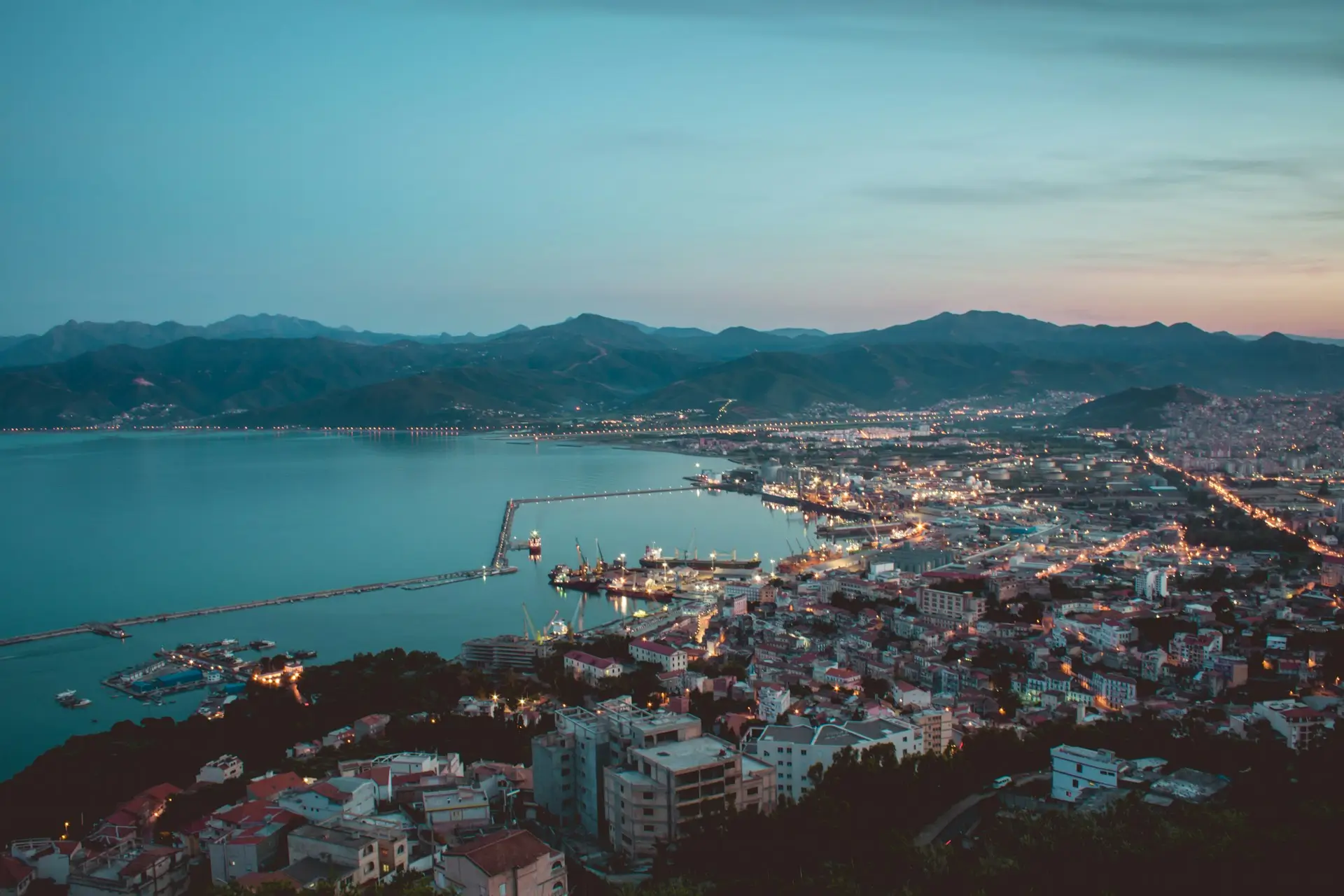
Algeria, recognized formally as the People’s Democratic Republic of Algeria, is located in North Africa along the Mediterranean coast. Spanning an area of about 2.38 million square kilometers, it holds the distinction of being the largest country in Africa and the tenth largest in the world. Algiers, the capital city, acts as the focal point for politics, economics, and culture within the nation. With a population surpassing 44 million, Algeria is home to a substantial number of people.
What to Know about Algeria’s Geography
Algeria is bordered by multiple nations, with Tunisia and Libya to the northeast, Niger to the southeast, Mali and Mauritania to the southwest, and Western Sahara and Morocco to the west. The Mediterranean Sea lies to the north. The geographical features of the country encompass expansive deserts, mountain ranges, and an extensive Mediterranean coastline. The Sahara Desert, which occupies a substantial part of Algeria, plays a crucial role in shaping its distinctive landscapes and diverse climatic regions.
Climate in Algeria
Algeria undergoes varied climatic conditions due to its extensive size and diverse geographical features. Along the northern coast, there is a Mediterranean climate characterized by mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers. In the southern regions, largely influenced by the Sahara Desert, the climate is semi-arid and arid, featuring scorching summers and scarce rainfall.
The Culture of Algeria
The cultural tapestry of Algeria weaves together indigenous Berber traditions and Arab-Islamic influences. In Algerian society, a profound emphasis is placed on the significance of family, community, and hospitality, with traditional customs and communal gatherings playing a vital role in daily life. Algerian music, notably Raï and Chaabi, enjoys popularity not only within the country but also resonates across the broader Maghreb region.
Religions Observed in Algeria
The predominant religion in Algeria is Islam, with Sunni Islam embraced by more than 95% of the population. Islamic principles and traditions exert a substantial influence on various facets of Algerian life, shaping family dynamics, cultural celebrations, and social norms.
Languages Spoken in Algeria
Arabic holds the status of the official language in Algeria, functioning as the primary means of communication in government, education, and media. Additionally, Berber languages like Kabyle and Chaouia are officially acknowledged and commonly spoken, particularly in rural areas, encompassing a significant portion of the population. Owing to Algeria’s colonial history, French continues to play a substantial role in business, administration, and higher education.
Algerian Human Resources at a Glance
Employment Law Protections in Algeria
In Algeria, the primary legal framework overseeing employment relationships is the Labor Code. Complementing this, other crucial rules and regulations, including the Constitution, laws designating legal holidays, and regulations overseeing social security, play a substantial role in shaping the employment landscape.
Employment Contracts in Algeria
In Algeria, employment contracts may take the form of either verbal or written agreements. There exist two main categories of employment contracts: fixed-term contracts and permanent contracts.
If there is no written employment contract, the assumption is that the employment relationship is of an indefinite duration.
Fixed Term Contacts for Algerian Employees
In Algerian employment practices, one is permitted to enter into a fixed-term employment agreement, whether on a full-time or part-time basis, under the circumstances outlined below:
- When the employee is engaged for tasks associated with non-renewable contracts of works or services.
- In cases where the individual is filling in for a regular employee during their temporary absence, with an obligation to maintain the job position.
- When the employing entity is required to carry out periodic tasks of an intermittent nature.
- If there is a justifiable need due to increased workload or seasonal requirements.
- When the nature of the work or activities is inherently of limited or temporary duration.
Fixed-term contracts must explicitly state the duration of the employment relationship and the reasons justifying the specified time frame.
Notably, there are no restrictions on the maximum duration or the number of renewals for fixed-term contracts.
Algeria's Guidelines Regarding Probation Period/Trial Period
The probationary period may extend up to six months, with the possibility of extending it to 12 months for individuals possessing high qualifications.
Throughout the probationary phase, the employee holds the same rights and responsibilities as their counterparts in equivalent positions. Additionally, this duration is taken into account when calculating their tenure within the organization if they are formally employed at the conclusion of the probationary term.
Either the employer or the employee retains the right to terminate the employment contract without compensation or advance notice during the probationary period.
Regulations and Rules Regarding Working Hours in Algeria
The standard workweek consists of 40 hours distributed across five working days. Each employee is entitled to a minimum of one day off per week, typically observed on Fridays in regular working conditions.
Under no circumstances should the daily working hours surpass 12 hours.
Algerian Laws Regarding Overtime
The permissible limit for overtime hours is capped at 20% of the standard working hours.
In the event that an employee is mandated to work beyond the regular hours, they are entitled to receive overtime compensation, which must be at least 150% of their standard hourly wage. Furthermore, should an employee be compelled to work on their designated day off, they should be granted a substitute day off and remunerated at a rate of 150% for the overtime hours rendered.
Termination
In Algeria, an employer is permitted to terminate a contract under only two circumstances:
- Gross misconduct
- Economic justification
Should an employer decide to terminate a fixed-term contract before its designated end, compensation for the remaining duration of the contract is mandatory.
In the case of termination for economic reasons in Algeria, the employer must undertake measures to mitigate the number of terminations, including:
- Implementing reduced working hours
- Introducing part-time work arrangements
- Enacting procedures for personnel retirement
- Facilitating the transfer of employees to other sectors within the company where they can further develop (employees who decline will be offered a severance package)
Algeria's Requirements Regarding Notice Periods
Employees who are terminated for reasons other than serious misconduct are entitled to a specified leave duration, with the minimum period determined by collective agreements or conventions. During this designated leave, the terminated employee is granted two hours per day of paid time, which can accrue, to facilitate the pursuit of new employment opportunities in Algeria.
Alternatively, the employer has the option to meet this obligation by compensating the terminated employee with an amount equal to the total remuneration they would have received during the same period.
Redundancy/Severance Pay in Algeria
Regarding redundancy benefits, the employer is obligated to provide an amount equivalent to three months’ salary to employees affected by downsizing and receiving unemployment insurance benefits.
This payment is determined by calculating the average gross monthly wage earned over the 12 months preceding the termination.
Employees terminated due to workforce reduction and compensated through another job, admission to retirement, or early retirement do not qualify for additional compensation beyond what is due for accrued paid leave.
No compensation is granted to employees terminated for gross misconduct.
Tax and Social Security Information for Employers in Algeria
Personal Income Tax in Algeria
In Algeria, personal income tax is computed using the following progressive rates:
| Annual Taxable Income (DZD) | Tax Rate % |
|---|---|
| Less than 240,000 | 0 |
| 240,001 to 480,000 | 23% |
| 480,001 to 960,000 | 27% |
| 960,001 to 1,920,000 | 30% |
| 1,920,001 to 3,840,000 | 33% |
| More than 3,840,000 | 35% |
However, this taxable income is eligible for a proportional 40% deduction from the overall income tax. The deduction is subject to a minimum of DZD 12,000 per year and a maximum of DZD 18,000 per year (equivalent to approximately DZD 1,000 to DZD 1,500 per month).
The tax rate applicable to bonus payments is 15%.
Payment returns and submissions to the DGI (Directeur Général des Impôts) in Algeria must be made by the 20th of the subsequent month. Simultaneously, the annual tax declaration is required to be submitted by April 30 each year.
Social Security in Algeria
In Algeria, social security is overseen by the CNAS (Caisse Nationale des Assurances Sociales des travailleurs salariés). Employers and employees are required to contribute the following percentages of the employee’s gross salary:
- Employers are mandated to contribute 26%,
- while employees are required to contribute 9%.
Employees’ contributions are deducted and transmitted by the employer. Employers are required to remit payments to the CNAS authority by the end of the subsequent month.
*The rates provided above serve as a general reference; actual rates applied may vary.
Important Information for Algerian Employees
Salary Payment
The legislation stipulates that employees must receive regular payments, and their wages should not fall below the nationally guaranteed minimum wage.
Annual Leave
Algeria’s leave cycle spans from July 1 to June 30, commencing on the first day of employment for new hires. Employees are granted 2.5 days of annual leave each month, with a maximum accrual of 30 days per year of service. Those in the southern states receive an extra 10 days of annual leave per year.
No employment relationships may be suspended or terminated during the annual leave period.
In the event of illness, employees are permitted to interrupt annual leave to avail themselves of sick leave and its associated rights.
Sick Leave
Employees are eligible for 15 days of paid sick leave at half salary, starting from the initial day of illness, and at full salary from the 16th day of illness or earlier if hospitalized.
Funding for sick pay and the reimbursement of medical expenses is sourced from the National Fund for Social Security, supported by contributions from both employers and employees.
Maternity & Parental Leave
Maternity Leave
Women employees are granted a maximum of 14 weeks of fully paid maternity leave. To qualify, they must cease working at least one week before their due date if they have met either of the following conditions:
- Worked a minimum of nine days or 60 hours in the three months leading up to the due date.
- Accumulated 36 days or 240 hours of work in the 12 months preceding the first medical confirmation of pregnancy.
Maternity pay is contingent upon the assistance of a recognized doctor or qualified professional during childbirth.
Paternity Leave
Male employees have the right to avail themselves of three days of paid paternity (emergency) leave following the birth of a child.
Special Leave
Employees are granted three days of paid leave for the following family-related events:
- Marriage of the employee
- Birth of the employee’s child
- Circumcision of the employee’s child
- Marriage of the employee’s descendant
- Death of the employee’s immediate family member or blood relative
- Death of the employee’s spouse
Additionally, once in their entire professional life, an employee is permitted to take 30 days of paid leave to perform Hajj.
Public Holidays
Normally, Algeria observes 11 public holidays each year, during which employees receive their full pay.
Benefits to the Employee in Algeria
Algerian Statutory Benefits
Employees are entitled to a range of benefits as stipulated by both legal provisions and collective agreements. These benefits encompass retirement pensions, annual leave, sick leave, maternity leave, paternity leave, special leave, and more.
Rules Regarding Visas and Foreign Workers in Algeria
General Information
Visas
The majority of visitors to Algeria are required to obtain a visa, which can be acquired at Algerian diplomatic offices, unless they are citizens of visa-free countries.
A limited number of nations, irrespective of their travel purpose, enjoy visa-free entry into Algeria for a duration of up to 90 days. Notably, Israeli citizens are excluded and are prohibited from entering, even in transit.
Various types of visas, such as tourist, business, transit, work, or student visas, must be obtained in person from an Algerian consulate or embassy before embarking on travel. The duration and validity of these visas are contingent upon the specific purpose of the visit.
Foreign nationals can apply for short-term visas to Algeria for various reasons, including tourism, business, cultural exchanges, and other temporary purposes. For those planning an extended stay, such as for study or work, the option of applying for Algeria long-term visas is available.
Work Permits
For legal employment in Algeria, foreign workers are required to obtain both an Algeria work visa and a work permit. Those intending to work in Algeria for a duration of fewer than 90 days can seek a temporary work visa, while those with long-term employment prospects must opt for a work visa.
During the application process for an Algeria work visa, applicants are obliged to submit a copy of their work contract. The local employer is expected to furnish a letter detailing the employee’s work title, position, and the purpose of their visit to the country. Additionally, the employer should explicitly state in the letter their commitment to covering the employee’s living expenses and repatriation costs.
Upon arrival in Algeria, foreign employees should initiate the process of obtaining a residency permit, which is essential for both working and residing in the country.
| Occasion | Date | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | New Year’s Day | January 1 |
| 2 | Amazigh New Year | January 12 |
| 3 | Eid al-Fitr | April 10 |
| 4 | Eid al-Fitr Holiday | April 11 |
| 5 | Labour Day | May 1 |
| 6 | Eid al-Adha | June 16 |
| 7 | Eid al-Adha Holiday | June 17 |
| 8 | Independence Day | July 5 |
| 9 | Islamic New Year | July 7 |
| 10 | Ashura | July 16 |
| 11 | Prophet Muhammad’s Birthday | September 15 |
| 12 | Revolution Day | November 1 |
Hire New Talent in Algeria
Our global recruitment services enable you to onboard personnel in any country without the financial commitment required for establishing a local entity.